Using HTTP proxies
If you are operating our Checkly Agent behind an HTTP proxy, for example in an enterprise environment, you can use an outgoing proxy for all check traffic. We recommend using the following setup.
Setting an HTTP proxy for your Private Location
We recommend storing the URL of your proxy in a global environment variable
so you can easily reuse it in your Private Location configuration and checks. In the example below we store it as PROXY_URL
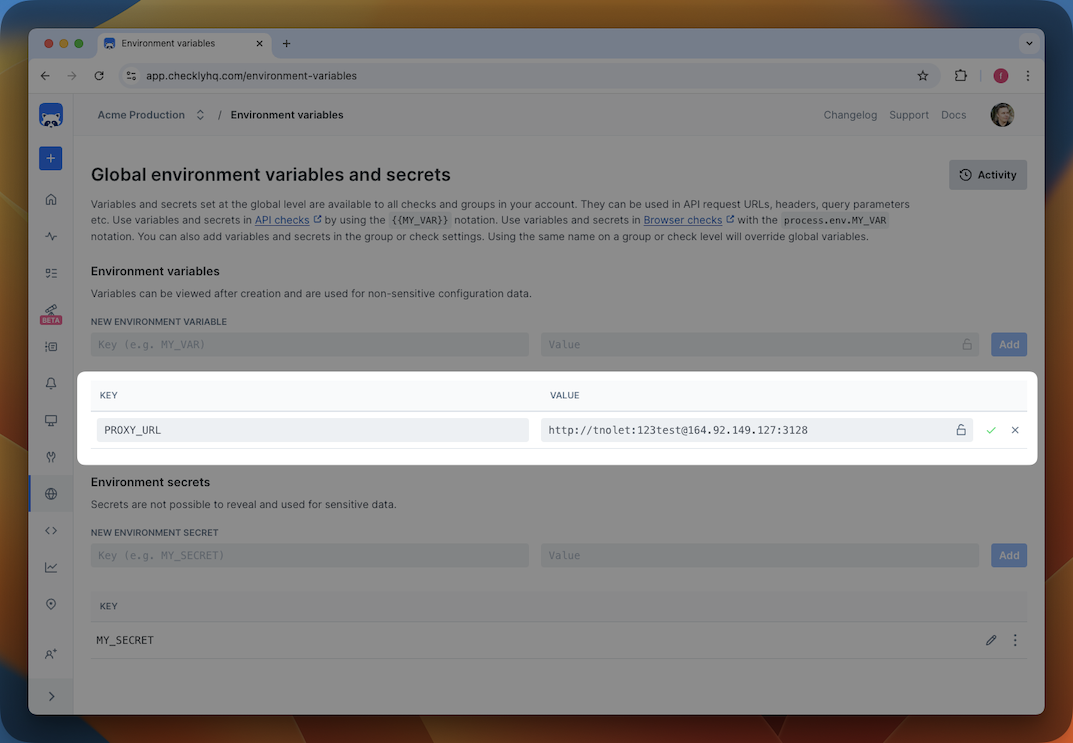
After this, you can reference this variable using {{PROXY_URL}} in the Private Location configuration.
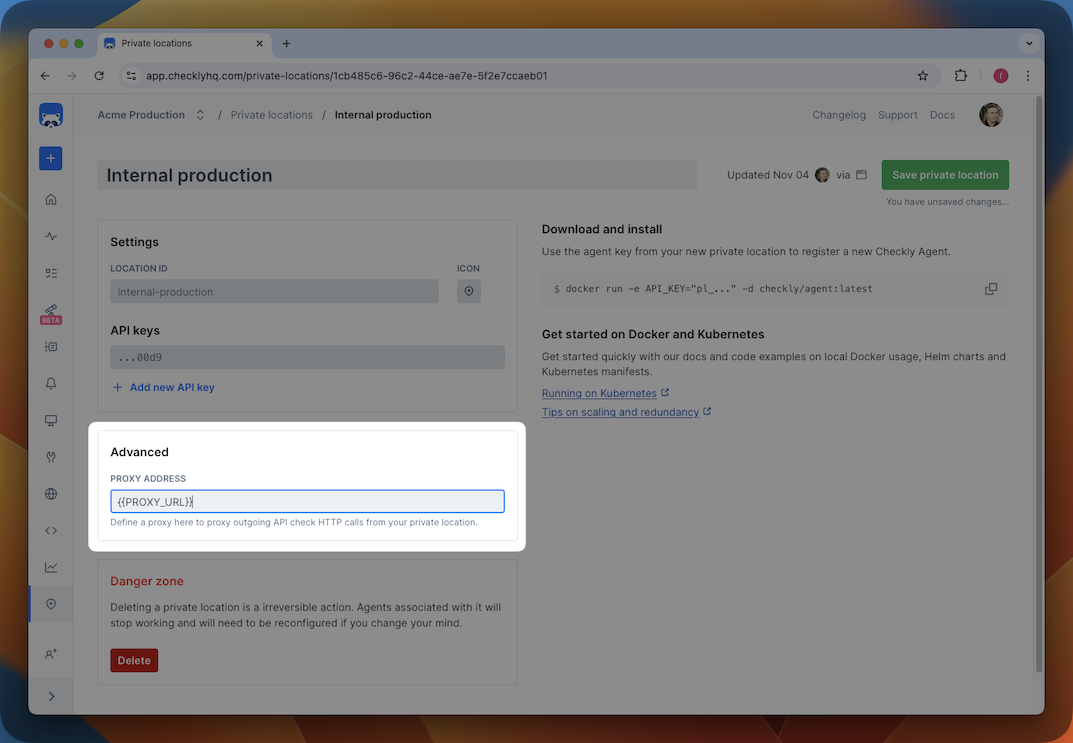
Using an HTTP proxy with API checks
With the setup complete, any API check which uses that Private Location will automatically inherit the proxy configuration for outgoing traffic.
Using an HTTP proxy with Browser checks
You can enable your proxy directly in your browser checks via a few extra lines of code, using the process.env.PROXY_URL
notation and Playwright Test’s test.use() method:
import { test } from '@playwright/test'
test.use({
proxy: {
server: process.env.PROXY_URL
}
})
test('Go to google.com', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https://google.com')
})
const { test } = require('@playwright/test')
test.use({
proxy: {
server: process.env.PROXY_URL
}
})
test('Go to google.com', async ({ page }) => {
await page.goto('https://google.com')
})
This is all that is required for a browser check to proxy all outbound network connections via your designated HTTP proxy. Check out both the Playwright networking docs and the Chromium network settings docs for some more information.
Last updated on November 18, 2024. You can contribute to this documentation by editing this page on Github